The #centexbelpatentcell conducted a search inspired by the EPO Patent Index 2023 and its specific report for Belgium, focusing on patents from Belgian companies related to textiles and plastics published in the last year.
The search unveiled that, in addition to patents concerning innovative processes or products, a number of patents were dedicated to waste minimization or waste valorization. A few of these patents are featured in the current month's selection.
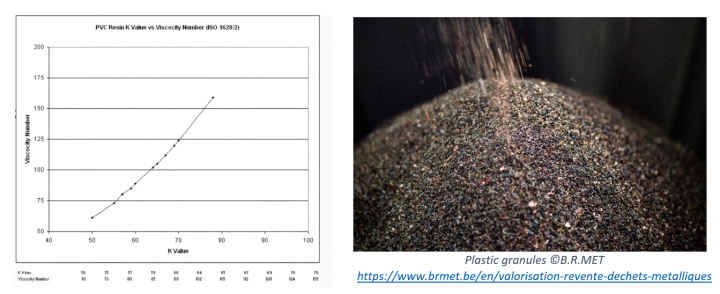
Micronized powder of recycled soft PVC and articles made therefrom
Patent number: EP4293067
Publication date: 2023-12-20
Applicant(s): Brussels Recycling Metal (BR Met) SA
Inventor(s): HUNTZ PIERRE-MARIE
Summary
The invention relates to the recycling of flexible PVC, in the form of micronized powder comprising at least 80% recycled flexible PVC, so as to be able to reintroduce it into processes for manufacturing PVC objects. Polyvinyl chloride, known by the abbreviation PVC, is a plastic polymer of very high consumption obtained based on petroleum derivatives and mineral chlorides (sea salt, hydrochloric acid, etc.). There are two types of PVC: rigid PVC, used for the manufacture of very many objects, articles, in all technical fields (pipes, credit cards, packaging, chassis, etc.), and flexible (or plasticized) PVC used in particular for the manufacture of textile fibers, bags of medical liquids, toys or for coating electrical cables. Recycling of the PVC at the end of its life is carried out by grinding in a shredder to form flakes which can then be re-extruded or used for injection molding. There remains the problem of the quality and reusability of the recyclate of flexible PVC, which does not allow the flexible PVC granules obtained in conventional forming processes such as extrusion, molding, etc. to be shaped in a satisfactory manner. The powder according to the invention or the granules according to the invention can be used to manufacture articles of recycled PVC.
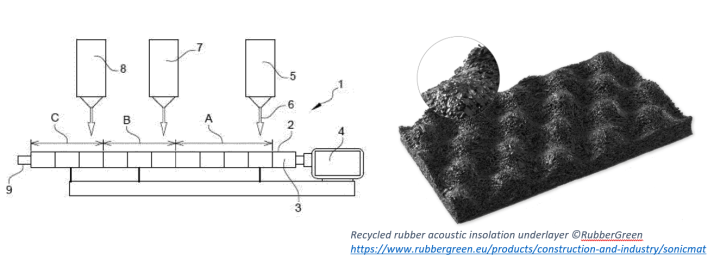
Method and device for producing recycled elastomer material to be crosslinked
Patent number: WO2023/161473
Publication date: 2023-08-31
Applicant(s): RUBBERGREEN INDUSTRIE SA
Inventor(s): SEGHAR SAID; PRUD'HOMME OLIVIER
Summary
The object of the present invention is to make it possible, from crosslinked waste, to produce rubber material ready for crosslinking, which is effective, and which is affordable in cost. To solve this problem, there is provided, according to the invention, a process for the production of ready-to-crosslink rubber material, comprising: a continuous extrusion of crosslinked rubber, in the form of grains and/or chips, comprising, preferably in succession, the following steps: (1) decrosslinking by mechanical shearing said grains and/or chips of said crosslinked rubber and increasing temperature until a decrosslinked paste is formed, (2) cooling the decrosslinked paste, and (3) mixing the cooled decrosslinked paste with at least one crosslinking agent, and collecting, at the outlet of this continuous extrusion, a pasty mixture forming said ready-to-crosslink rubber material, in particular during molding. This process makes it possible to produce, in a continuous extrusion process, both the decrosslinking of the treated rubber granules or chips, the cooling of the resulting paste and the mixing of the compounded paste with at least one crosslinking agent, in particular accelerators and activators, which continuously gives a rubbery material ready for crosslinking, which can immediately be transferred to moulds or other shaping elements where crosslinking takes place.
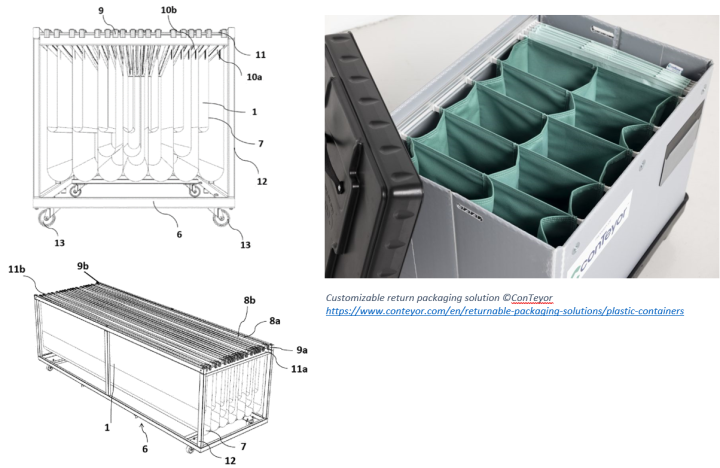
Recyclable textile for packaging, transporting and/or storing items
Patent number: WO2023/214037
Publication date: 2023-11-09
Applicant(s): CONTEYOR INTERNATIONAL NV
Inventor(s): VAN NECK PETRA
Summary
The present invention relates to a textile and a container comprising said textile for packaging, transporting and/or storing items. Specialized forms of packaging, such as automotive parts packaging, require specialized packaging material as the parts may be heavy and fragile and include many electrical and electronic components. The parts are more prone to damage during transit, loading, and unloading and are in need of extra protection. As various parts have to travel long distances, they have to be packaged such that they reach the manufacturer in a safe-to-use condition. The invention relates to a textile suited for packaging, transporting and/or storing items, wherein said textile is a multilayered textile, said multilayered textile comprising a reinforcing middle part, a first outer nonwoven layer and a second outer nonwoven layer, wherein said reinforcing middle part is sandwiched between said first outer and said second outer nonwoven layer, wherein said reinforcing middle part is comprised of two superimposed scrim layers, wherein each of said scrim layers has a weight between 50 to 100 g/m2 and said textile has a total weight of between 250 and 350 g/m2 as measured by EN 9073-1: 1992. Said textile is sufficiently strong to withhold the weight of heavy items and is sufficiently flexible and soft to be used a packaging material for packaging items prone to scratches. The current invention also relates to a container comprising aforementioned textile.
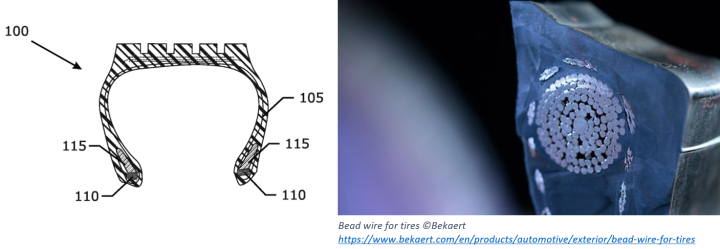
A method to recuperate a bead bundle assembly out of an end-of-life tire
Patent number: WO2023/110369
Publication date: 2023-06-22
Applicant(s): BEKAERT
Inventor(s): TIAN HAO; LUO YIWEN
Summary
The invention relates to a method of recuperating a bead bundle assembly out of an end-of-life tire. The invention also relates to a bead bundle assembly out of an end-of-life tire and its application. Every year there are about 1 billion end-of-life tires worldwide. A radial tire normally comprises a tread, at least one belt layer, at least one carcass layer and a pair of beads, wherein the belt layer and carcass layer are reinforced by steel cords or polyester cords, the bead is reinforced by a bead ring formed by a steel wire or a group of steel wires wound as a bundle. One of the recycling ways is recycling the rubber, the rubber of the end-of- life tires is recycled by being converted into new materials, fuels or recycled rubber. Another of the recycling ways is recycling the tire, the tire is re-treaded to be a new tire. The tread of the end-of-life tire is removed, and a new tread is rebuilt, as thus a tire is recycled. A third of the recycling ways is recycling the bead wire, the bead wire is drawn out of the tire for recycling the steel. The rubber of the tire can also be recycled after the recycling of the bead wire. It is still desired to have more recycling ways to optimize the value of an end-of-life tire. The present discloses a method of recuperating a bead bundle assembly out of an end-of-life tire is provided, the method comprises several steps including: selecting an end-of-life tire having a tire identification; taking out the bead bundle assembly with or without a rubber layer remaining thereon, without plastic deformation of the bead bundle assembly; identifying each bead bundle assembly with at least said tire identification; and finally storing the bead bundle assembly. The invention provides a solution of optimizing the value of an end-of-life tire.
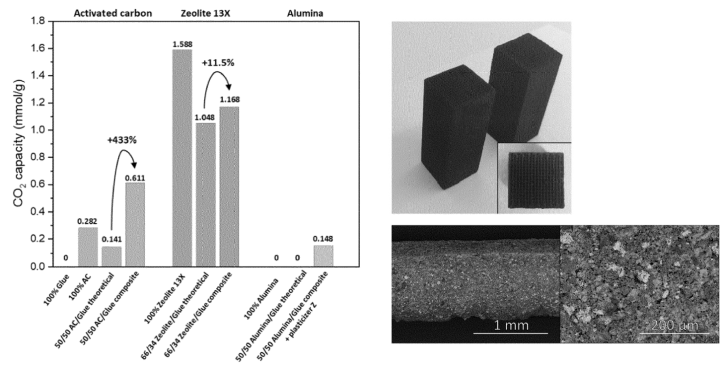
A carbon dioxide capture structure and a method of making thereof, and a method for removing carbon dioxide from a fluid
Patent number: EP4249113
Publication date: 2023-09-27
Applicant(s): VITO NV
Inventor(s): BEN SUTENS; MARLEEN ROMBOUTS; YORAN MICHEL MARC ARIELLE DE VOS
Summary
The invention relates to a carbon dioxide capture structure having a monolith three-dimensional shape. The invention also relates to a method of making a carbon dioxide capture product, a method for removing carbon dioxide from a gas or fluid mixture, a system for removing carbon dioxide from a gas or fluid mixture, and a packed bed comprising a plurality of carbon dioxide capture structures. Some processes may help reducing the ecological impact of CO2 by capturing it preventively as well as using it as a building block for fuels, polymers and other valuable chemicals, also known as Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS). CO2 could be captured directly out of air (Direct Air Capture) as well as out of industrial flue gases. Typically, CO2 capture processes involve the use of liquid amine solutions. However, these amines may have several drawbacks including high energy consumption during regeneration, thermal and oxidative solvent degradation and evaporation, as well as formation of corrosion products. The invention provides for a carbon dioxide capture structure having a monolith three-dimensional shape, the structure being porous with interconnected pores which are accessible from an exterior side of the structure, wherein the structure is made of a build material comprising a first material and a second material, wherein the first material is a sorbent material and/or a support material (preferably functionalizable for carbon dioxide adsorption), and wherein the second material is a binder material including potassium silicate. The invention also relates to a method of making said carbon dioxide structure and a method for removing carbon dioxide from a gas or fluid mixture.
Expanded moulded parts made of natural fibres
Patent number: WO2024/038006
Publication date: 2024-02-22
Applicant(s): CORKCONCEPT SA
Inventor(s): LAZKO JEVGENIJ; NARINX ALEXANDRE; YADA-COUTURIER BOPHA; DUBOIS PHILIPPE; LAOUTID FOUAD
Summary
The invention relates to the manufacture of rigid insulating materials, preferably 100% natural and/or biosourced, having a better thermal coefficient than existing sheets made of natural and/or plant fibres, which materials are biodegradable and easy to work with. Whether for packaging or construction applications, there are insulating materials, in the form of panels or flexible layers based on natural materials, such as natural fibers. Nevertheless, the insulating performance of such materials is often disappointing compared with conventional synthetic materials such as polystyrene or polyurethane, or mineral materials such as glass wool. These materials are often soft and cannot be grooved, and are difficult to cut sharply. In fact, it is very difficult to form a panel that is sufficiently strong and based on natural fibers, without adding at least one thermoplastic binder or other synthetic additive to it, in order to secure the fibers together, and/or facings on each side of the material in order to ensure cohesion thereof, which then makes it impossible to recycle or compost such panels.
The invention relates to an expanded molded part made of cellulosic and/or lignocellulosic fibers, the surfaces of which are a crust enclosing an open-porosity structure, the constituents of the crust and of the open-porosity structure being identical. Unlike expanded synthetic materials such as polyurethane or polystyrene, in which the air is captured in closed bubbles, the expanded part of the invention has an open porosity, that is to say that the air can circulate in the material, between the fibers, thus giving it perspiring properties. The invention also relates to the method of manufacturing the molded part of the invention. It includes the steps of: (1) mixing cellulosic and/or lignocellulosic fibers, at least one binder, at least one foaming agent, and water; (2) introducing the resulting mixture into a mold; and (3) heating the mold to a temperature preferably between 100 °C and 150 °C.
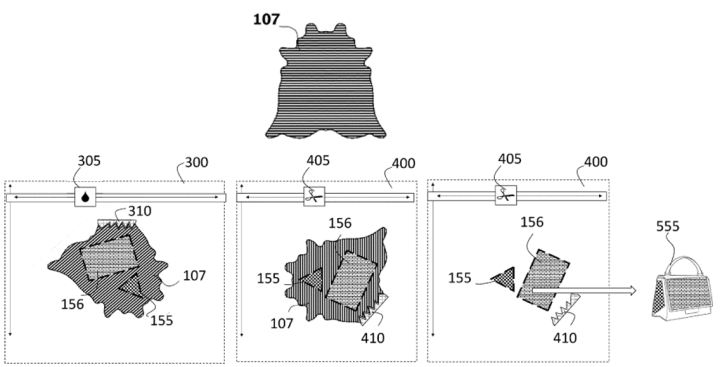
Manufacturing a decorated leather article
Patent number: WO2023/222591
Publication date: 2023-11-23
Applicant(s): AGFA NV
Inventor(s): DONDERS MARK; JANCART DIETER
Summary
The invention is related in the technical field of manufacturing decorated leather articles whereof one or more flat leather parts of said leather article are decorated with inkjet printing technology. Leather by itself is already perceived as a luxury product, but personalization and customization, for example by decoration, can further enhance this luxury feel. The decoration may be done after the manufacturing of the leather article but also decorated hides by inkjet technology may be cut into flat leather parts which are connected (e.g. sewed) together for forming a leather article, such as a shoe or handbag. By inkjet printing on hides, the possibilities for decorating the leather articles before the sewing becomes possible. The present invention provides therefor mechanically an alignment means on the hide which is used to align on both supports so to avoid said inefficient decorating flat leather parts of leather articles by inkjet printing. These and other objects of the present invention will become apparent from the detailed description hereinafter. The mechanical application of said alignment means on the applied leather obtain a more efficient and economical method of manufacturing high quality decorated natural leather articles allowing personalization and customization and having a short delivery time to the customer, as high delivery times reduce the luxury feel.
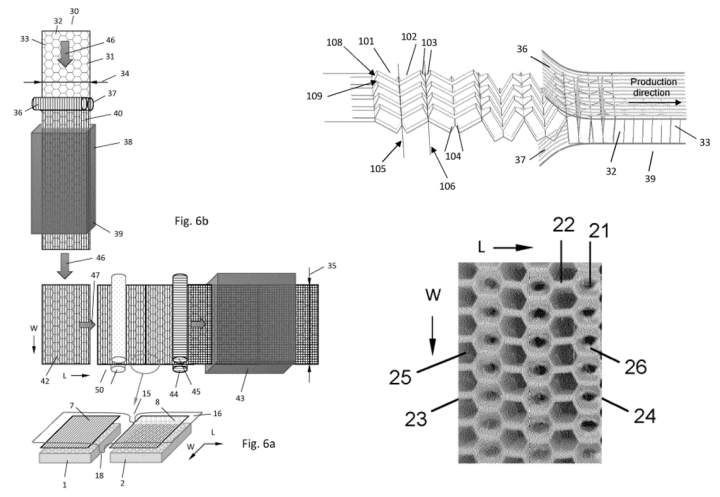
Sandwich panel with unidirectional composite tapes and its production process
Patent number: EP4302986
Publication date: 2024-01-10
Applicant(s): ECONCORE NV
Inventor(s): PFLUG JOCHEN
Summary
The present invention relates to optionally large width thermoplastic sandwich panels with composite skins in a 0/90° unidirectional tape layup as well as to the production thereof. The inline lamination of continuously reinforced thermoplastic composite skins onto a thermoplastic honeycomb core results in cost efficient sandwich panels which provide stiffness and strength at minimal weight for use in a wide range of applications in many industries. Typically, woven thermoplastic composite skins or two layers of unidirectional fiber reinforced thermoplastic tapes (UD-tapes) in a 0°/90° layup are applied on each major surface of the honeycomb core to create a sandwich panel with high bending stiffness and strength in both principal directions of the panel. Continuously produced thermoplastic honeycomb cores enable the in-line production of such sandwich panels. Two layers of thermoplastic tapes are typically laminated together in a double belt laminator and rolled up to form a skin laminate. Such laminates are then laminated onto both sides of the honeycomb core, e.g. in-line during the production of the continuously produced thermoplastic honeycomb core to form composite skins. The present invention enables the production of an optionally large width thermoplastic sandwich panel with composite skins in a 0/90° unidirectional tape layup. The composite skins can be composed of thermoplastic film or sheet material. The present invention allows rapid production of different widths of completed thermoplastic honeycomb sandwich panels. Thermoplastic film or sheet is preferably joined/laminated by thermoplastic welding to a honeycomb core.