Classification
According to domestic or commercial use
A floor covering has to meet specific requirements according to wear and appearance retention. The minimum requirements depend on the setting where it will be used (at home (domestic use) or in offices, shops, public places (commercial use)) and on the intensity of use (occasional, moderate, heavy).
The Vetterman test simulates and assesses appearance change due to traffic. Therefore it is an important test to assess whether a floor covering answers to the requirements of the domestic commercial use class and the intensity of use within these classes.
Use class: domestic or commercial
Domestic use
Light or occasional use (21)
Suited for bedrooms
Medium use (22)
Suited for living rooms, kitchen, children and hobby rooms
Medium to heavy use (22+)
Suited for intensive use in living rooms, kitchens, corridors...
Intensive use (23)
Suited for heavy use at home
Commercial use
Light or occasional use (31)
Suited for use in hotelrooms
Medium traffic (32)
Suited for use in offices, stores, class rooms...
Intensive traffic (33)
Suited for use in lobbies (banks, hotels, town halls), restaurants...
Heavy use (34)
In order to get a “heavy use” 33 commercial use classification special requirements with regard to cut edge strength have to be met.
Luxury classes
Floor coverings may vary in luxury aspects.
The rating goes up from 1 to 5 (highest ranking).
Additional requirements and tests
Floor coverings have to meet a variety of additional requirements according to the intended use. Below you will find an overview of the most important ones and the tests Centexbel carries out in view of classification.
Castor chair suitability
If a floor covering is used in an office, it has to be resistant to the wear of rolling wheels of castor chairs.
The castor chair test assesses the durability of a floorcovering by simulating the conditions that it would be subjected to in real use.
Stairs suitability

A carpet on stairs is subject to the forces imposed by a person going up and down a staircase that are very different from the forces imposed by the same person when walking on a flat surface. The most vulnerable part to physical abrasion is the nosing
Electrical resistance
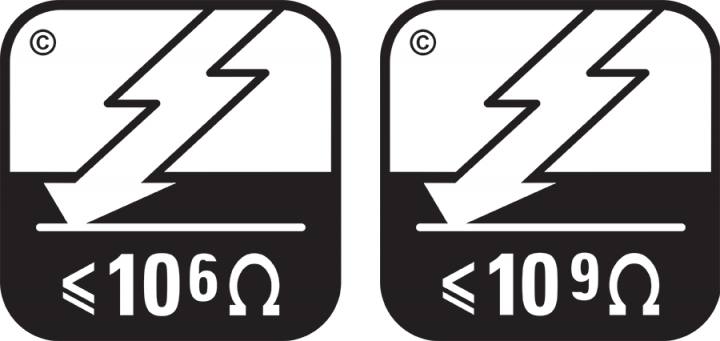
Static dissipative floor coverings allow static electricity to 'dissipate', or discharge in a controlled way. They are used in rooms needing a higher level of static control, such as in computer rooms, x-ray suites, operating theatres and some electronics manufacturing facilities. A static dissipative floor is defined as having a surface resistance of between 1 x 106 ohms and 1 x 109 ohms.
Static conductive floor coverings are more conductive than static dissipative floors and are used in places where very sensitive components are being handled, such as on electronic assembly lines. Conductivity is improved by installing the floor over a grid of copper tape and earthing it to the ground. The surface resistance of static conductive floors is defined as being between 4 x 104 ohms and 1 x 106 ohms.
Antistatic behaviour
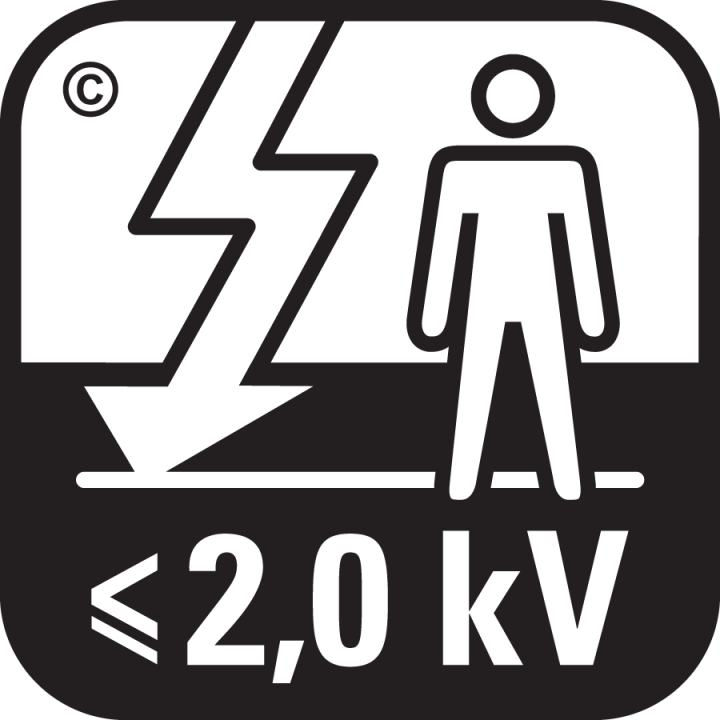
Shoe soles and clothing become electrically charged, with this charge being transmitted to the wearer. The static electrical charge depends on the type of materials coming into contact with each other and on the humidity. With dry air / low humidity conditions materials and people are more electrostatically charged than with high humidity levels.
Electronic components are especially susceptible and may cause switching errors or even become irreparably damaged by minor electrostatic discharges that are not even noticed by people. Electrostatic charging can be reduced through the selection of suitable materials and by increasing humidity levels where too low, although it cannot be completely prevented.