Now that the federal safety council is gradually re-opening the country and restoring economic activities, the wear of masks is being recommended - and in some instances even mandatory - whenever it becomes difficult or even impossible to respect social distancing. On this page we recapitulate our testing scope, the most important information on the different types of masks, and the measures taken by the Belgian government on the ATP (Alternative Test Protocol) of medical masks.
We also illustrate the two most important requirements in the face of protection against the coronavirus, i.e. Bacterial Filtration Efficiency and Breathability. Finally we wish to give some do's and don'ts about the correct use (handling) of masks.
The purpose of medical face masks
Our microbiological lab in Grâce-Hollogne is the only accredited laboratory in the Benelux that is equipped to test face masks worn by the medical and care staff to protect patients or residents of care homes from pathogens spread by the medical staff.
A surgical mask is a medical device covering the mouth, nose and chin ensuring a barrier that limits the transition of an infectious agent between the hospital staff and the patient. It was originally developed to contain and filter large droplets of microorganisms expelled from the mouth and nasopharynx of healthcare workers during surgery, thereby providing protection for the patient.
Medical face masks can also play an important role in reducing the spread of a viral disease by protecting persons at risk from infections caused by hand-mouth or hand-nose contact and by protecting people in the vicinity of infected persons from droplet contamination by pathogens ejected during coughing and sneezing.
What are the requirements for a reliable and safe medical mask?
In Europe, surgical masks must wear a CE-mark and comply with the requirements defined in EN 14683: Medical face masks - Requirements and test methods.
The standard defines surgical masks as: medical devices, covering the mouth, nose and chin ensuring a barrier that limits the transition of an infectious agent between the hospital staff and the patient.
In respect of the performances, the mask is tested as a final product and has to comply with different requirements.
The classification of the masks is based on the results from the following tests:
- bacterial filtration efficiency (BFE)
- breathability (delta P)
- splash resistance (synthetic blood)
- microbial cleanliness
- biocompatibility
Because surgical masks are considered medical devices of class I, the manufacturer has to run a risk analysis and additional tests if needed to respond to the European Medical Device Regulation 2017/745.
There are no requirements regarding barrier against inert particles.
Medical masks used in the USA are submitted to the same tests as the ones described in the European standard EN14683, except that the FDA also prescribes the measurement of filtration efficiency regarding inert particles (latex) and fire tests.
The US standard ASTM F2100-11 Standard specification for performance of material used in medical face masks describes the tests and requirements with which the materials have to comply that are used to produce the masks. Several tests are not run on the final product, but on the different materials have to be tested together in the way they will be used in the final mask.
The performances of the materials composing the mask are evaluated by five tests :
- bacterial fitlration efficiency
- breathability (delta P)
- splash resistance
- particle filtration efficiency
- fire test
According to the results, the masks are classified in three levels.
Read the article on "surgical mask performances" by Yvette Rogister & Mark Croes
Surgical masks and comfort masks: ATP
The COVID-19 epidemic is hampering the supply of various healthcare materials, including medical devices such as surgical masks. The Federal Agency for Medical and Health Products (FAMHP) inspection services note that in many cases, the surgical face masks that are offered are not provided with the necessary declarations, certificates and test reports that unambiguously demonstrate that they meet the requirements of the applicable European standard (EN 14683:2019 + AC:2019) or one of the international standards that are currently also exceptionally accepted (ASTM F2100, YY 0469:2011 and YY/T 0969-2013).
To cope with the shortage the FAMHP has drafted an Alternative Test Protocol (ATP) based on preliminary studies performed by Centexbel.
The ATP only looks at the results for Bacterial Filtration Efficiency and Differential Pressure. These are the most important parameters in the current context.
Centexbel, the only accredited laboratory in the Benelux that can test face masks according to the European standard EN 14683, has investigated the correlation between these two parameters over the past weeks.
The indications provided by this study have been taken into account when drawing up this ATP.
Depending on the results according to the ATP, face masks can be used either as surgical face masks or as comfort masks.
What is the difference between a surgical mask and an FFP mask?
Medical face masks are subject to the Regulation (EU) 2017/745 on Medical Devices and must meet the requirements defined in EN 14683. They primarily protect patients and persons in need of care from possible pathogenic agents spread during treatment by medical/care staff.
FFP (filtering face piece) respiratory masks are considered PPE and are therefore subject to the Regulation (EU) 2016/425 for Personal Protective Equipment. FPP masks must meet the specifications of EN 149. FFP masks protect healthcare workers from being infected by airborne pathogens spread by patients. There are different protection levels for respiratory masks (FFP 1-3), depending on their level of protection against the penetration of dust, liquid or solid particles and pathogens.
Read more on the different types of face masks!
Please note that Centexbel is not accredited to test FFP masks.
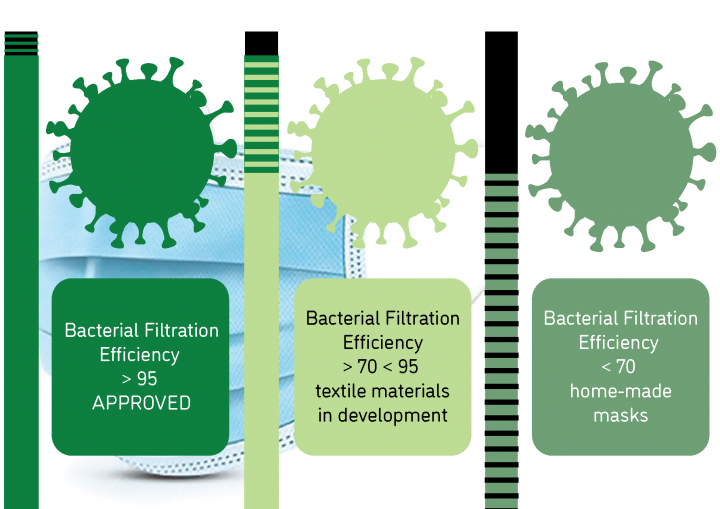
What is the protection level of community masks against the coronavirus?
What is Bacterial Filtration Efficiency?
In order to be called a medical/surgical mask, a minimum 95% filtration rate is required. Moderate and high protection masks have bacterial filtration rates of 98% to greater than 99%.
Although the fact that some fabrics we have tested - in view of community masks - obtained a 99% filtration rate, they were too closely structured to offer the necessary breathability (air permeability).
The EN 14683 standard method measures the effectiveness of a surgical mask in capturing aerosol droplets containing bacteria. The filtration efficiency depends on the particles or bacteria size, the air flow passing through the mask and the surface properties of the particles.
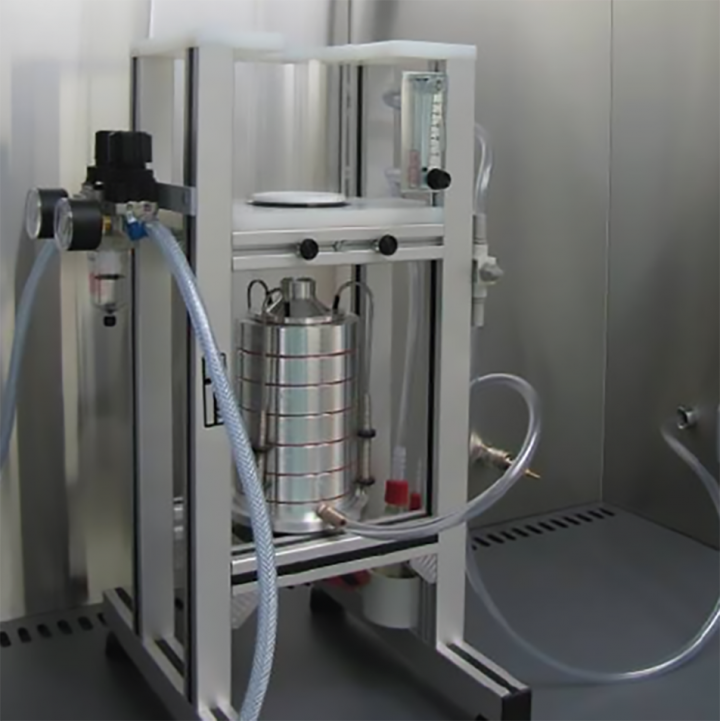
Principle
A specimen of the mask is inserted between an impactor and the chamber where the bacterial aerosol is produced. The bacterial aerosol (Staphylococcus aureus) arrives in the chamber "aerosol", goes through the specimen and is recuperated on Petri dishes placed in the impactor.
The efficiency of filtration of the mask is given by the percentage of bacteria that are stopped by the mask specimen, compared to a trial performed without specimen.
Depending on the type of facial mask, the required filtering levels are ≥ 95 % or 98%.
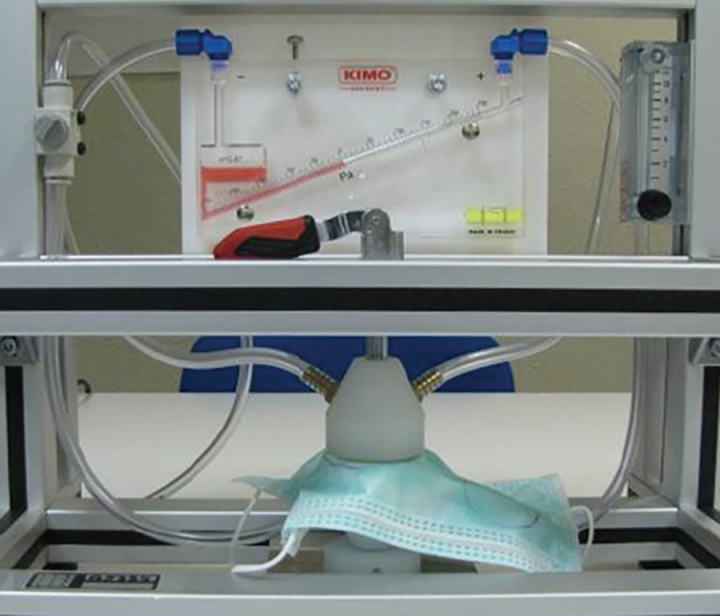
What is Differential Pressure or breathability?
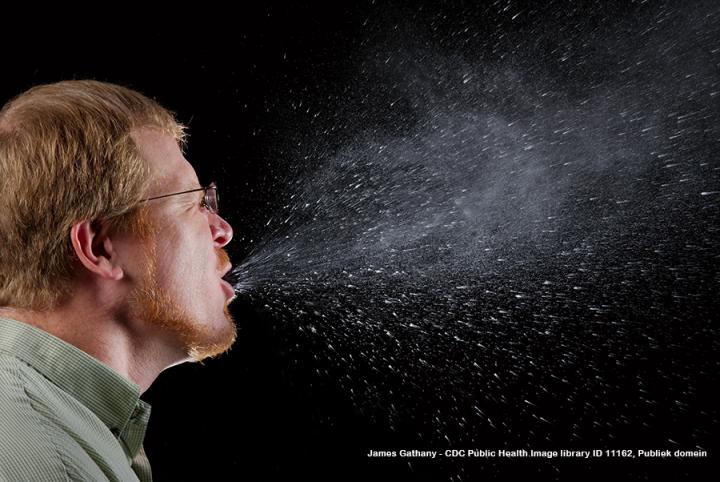
An average sneeze or cough can send around 100,000 contagious germs into the air at speeds up to 100 miles per hour.
"The virus spreads over mountains and oceans. That a mask could stop it is a utopia," said Maggie De Block, the Belgian Minister of Public Health, a while ago on television. Today she sticks to that. "We've said many times that such masks don't protect yourself but others. It's an additional barrier, but it won't stop the virus. It gives a false sense of security, but it's good if you can't keep your distance."
This method measures the pressure drop across a surgical mask under specific conditions of airflow, temperature and humidity. The differential pressure is an indicator of the breathability of the mask, expressed in a differential pressure (∆P) in mm H2O/cm2 or Pascal/cm2.
“the differential pressure is an indicator of the breathability of the mask”
A differential pressure of viz. < 29,4 or < 49,0 Pascal/cm² is required for surgical masks of Type I and Type II.
The breathability of a surgical mask or its properties to let air through depends on a series of parameters such as the nature of the textile, the applied finish, the number of layers or its thickness.
How to put on a (surgical) face mask?
- Before putting on a face mask, wash your hands for at least 20 seconds with soap and water, or rub your hands thoroughly with alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Check for defects in the face mask, such as tears or broken loops.
- Position the colored side of the mask outward.
- If present, make sure the metallic strip is at the top of the mask and positioned against the bridge of your nose.
- If the face mask has:
- Ear loops: Hold the mask by both ear loops and place one loop over each ear.
- Ties: Hold the mask by the upper strings. Tie the upper strings in a secure bow near the crown of your head. Tie the bottom strings securely in a bow near the nape of your neck.
- Dual elastic bands: Pull the top band over your head and position it against the crown of your head. Pull the bottom band over your head and position it against the nape of your neck.
- Mold the bendable metallic upper strip to the shape of your nose by pinching and pressing down on it with your fingers.
- Pull the bottom of the mask over your mouth and chin.
- Be sure the mask fits snugly.
- Don’t touch the mask once in position.
- If the mask gets soiled or damp, replace it with a new one.
Do not:
- touch the mask once it’s secured on your face, as it might have pathogens on it
- dangle the mask from one ear
- hang the mask around your neck
- crisscross the ties
- reuse (professionally non-decontaminated) single-use masks
If you have to touch the face mask while you’re wearing it, wash your hands first. Be sure to also wash your hands afterward, or use hand sanitizer.