Applicant: SIOEN INDUSTRIES NV
Inventor: Willem VAN DAELE, Frank VERANNEMAN, Joost WILLE JOOST, Bruno DEVOS
Patent application number: EP4151812
The problem
Reinforcement fabrics can be formed by a scrim (also called mesh) which may or may not be encapsulated in a thermoplastic or elastomer coating. The fabric structure makes the encapsulation or coating process easier by providing greater interim spaces. These types of reinforcement fabrics can be useful for roofing membranes, tents, tarpaulins, placards, banners, advertising signs and the like.
One of these types of reinforcement fabric for use as roofing material is known from patent publication no. US 10.072.419 B2. In applying the roofing material, the roofing material is secured using plugs. The disadvantage of these types of fabrics is that through the uplift as a result of wind load, the fixation points may tear out under extreme wind loads.
The solution
The current invention provides a reinforcement fabric with improved tear resistance that also reduces the possible uplift under the wind load.
The invention is a reinforcement fabric for synthetic membranes for application in roofing, comprising a coated reinforcement fabric or a roofing material including the former.
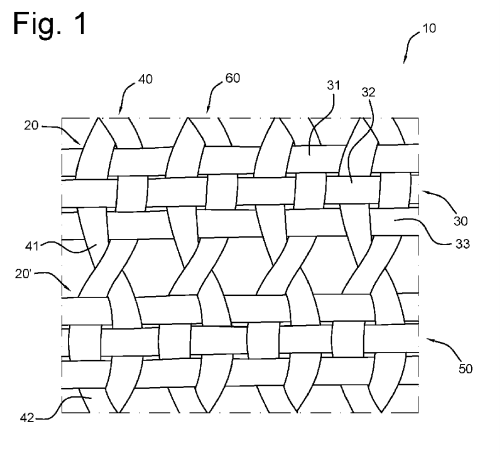
The reinforcement fabric for roofing materials comprises scrim, in the form of a woven mesh, whereby the open scrim has a number of bundles of weft threads located at a distance from each other in a first direction, and a number of bundles of warp threads at a distance from each other in a second direction, approximately perpendicular to the first direction, whereby the bundle of weft threads cross the bundle of warp threats at intersections.
Each intersection is made up of at least one pair of warp threads woven into at least two weft threads, whereby each pair of warp threads is woven into the bundles of weft threads in a half-cross leno weave, such that the warp threads only cross each other between adjacent bundles of weft threads. Within the context of this description the term "half-cross leno weave" refers to a leno weave of warp threads that only cross each other once between adjacent bundles of weft threads. Preferably, all warp threads are woven into the bundle of weft threads. In addition, in each intersection, the weft threads are woven with the warp threads in a weave pattern, preferably in a linen weave, twill weave or satin weave.
The inventor has found that these combinations of half-cross leno weave with a uniform weave, preferably a linen weave, twill weave or satin weave between the intersections of the leno weave has a reduced inweave compared to known weave structures, such as that published in US 10.072.419. The reduced inweave is achieved by the keeping the inweave as limited as possible, whereby the threads are lie stretched within the plane which reduces the extension with possible uplift. Through this, the uplift is reduced during wind load because the fabric is kept as flat as possible.
In addition, a fabric is created with a thickness that is the same as the thickness of the knitted scrims and is thus thinner than a standard woven fabric. So, it can be used as a roofing material with fewer fixation points with the same resistance to wind load. This is, on the one hand, a cost saving on material and on the other hand, a cost saving of the required work time of the installer.
The coated fabric consists of a reinforcement fabric and a coating consisting of a thermoplastic or elastomer material, whereby the coating is located along the length of the weft threads and the warp threads and is located between the weft and warp threads at the intersections. During the coating of the reinforcement fabric, a layer is applied in the form of a paste on one or both sides of the reinforcement fabric. Direct coating is one of the most used techniques and is based on the application of one or more layers of thermoplastic or elastomer material on the reinforcement fabric using a scraper, knife-coating or kiss roll coating. The coating can be applied in various ways, such as using extrusion coating, pultrusion or impregnation using padding.